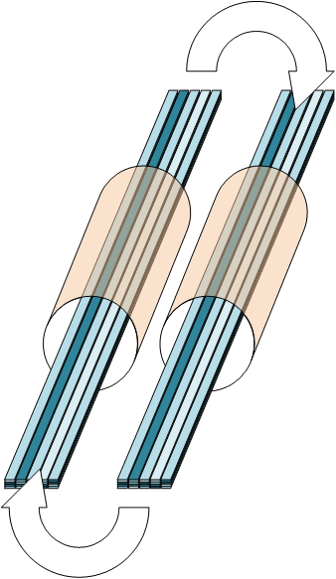
The idea behind the PowerMaglev project came from two fundamental considerations.
One basis was the recurrent statements in the media that the use of second-generation superconductors was actually possible. However, the problem is the arrangement of the superconductors as a replacement of conventional conductor materials because of the lack of flexibility of the high-temperature superconductors during installation.
The basic construction of the PowerMaglev is dominated by long, straight sections. Only at the beginning and at the end of the coil segments special arrangements are necessary. By this simple straight construction so a major problem in the use of superconductors should not occur.
The current status is estimated as follows:
The high-temperature superconductors are offered and manufactured worldwide by several manufacturers.
In all developments, it can be seen that they are strip conductors with more or less different layer structure. The layer thickness of the actual superconductor is not greater than 5 microns. The width of the strip conductors depends on the product and is approx. 4.0 mm to 12.0 mm.
In the development of high-temperature superconductors is currently mainly a cheap production and stable parameters at increasingly higher currents of the individual superconductors.
For the realization of the project PowerMaglev a cost-effective production of superconductors is advantageous.
Research on achieving large and largest flows per superconductor could have a positive impact on the PowerMaglev project as a secondary effect.
Status of the project PowerMaglev:
As is well known, it can be assumed that the superconducting state is governed by the factors electricity; Temperature and magnetic flux density depends.
However, in the case of high-temperature superconductors, the direction of the magnetic field also has a significant influence.
This directionality of the magnetic field must also be seen in the context of temperature.
In preparation of the project, the influence of the magnetic field around and in the parallel superconductors will be investigated (so far the superconductors have been considered as an idealized conductor).
Goals are currently seen:
- Proof that the project idea works.
- To be able to agree on the required technical parameters for the use of available superconductors.
- The mechanical design to optimize the superconductor.
It is believed that an arrangement of several superconductors on an insulating basis is an essential prerequisite for a cost-minimized production of superconductors. This makes it relatively easy to produce the high number of superconductors required. This approach must be placed with the manufacturers.
The system components required for energy input and output required by S-MES are not considered in more detail in the application-related study. It is assumed that appropriate solutions are available. To optimize the efficiency, it is intended to achieve the high total current with as many small currents (about 100 A) per superconductor. At the interface between the coil segments and the input and output, the current should be relatively low. This is to avoid high power losses at the necessary subsequent facilities.